顳上溝
| 此條目可參照英語維基百科相應條目來擴充。 (2021年6月3日) |
| 顳上溝 | |
|---|---|
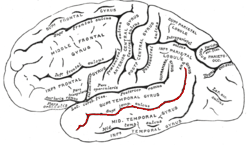 左側大腦半球外側(顳上溝位於紅色標記處) | |
 左側大腦半球外側(顳上溝位於紅色標記處) | |
| 基本資訊 | |
| 屬於 | 顳葉 |
| 標識字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | sulcus temporalis superior |
| NeuroNames | 129 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.145 |
| TA2 | 5494 |
| FMA | FMA:83783 |
| 《神經解剖學術語》 [在維基數據上編輯] | |
顳上溝(英文:Superior temporal sulcus)是大腦顳葉的一條腦溝,分隔了顳上回和顳中回[1][2]。顳上溝與人腦的社交能力緊密相關(心智理論),包括理解他人的語言、動作和表情等[3][4]。
結構[編輯]
顳上溝在外側溝之下,分隔了顳上回和顳中回[2]。顳上溝在左右大腦半球呈現不對稱分布,左側大腦半球的顳上溝較長,而右側大腦半球的顳上溝較深[5]。
功能[編輯]
語言處理[編輯]
當聽到人的聲音時,顳上溝區域變得活躍。許多研究顯示顳上溝與處理語句、詞組、音位等緊密相關[1][5]。此外,在進行手語交流時,位於額葉的布若卡氏區會被激活,但布若卡氏區會接收來自顳上溝的信號[6]。
社交能力[編輯]
顳上溝與人的社交能力有關,可分辨人聲和環境聲音、有條理的故事和雜亂的語言、生物體運動(包括臉部表情)、他人注意力和情感等[1][4]。
臨床[編輯]
參見[編輯]
參考資料[編輯]
- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Superior Temporal Sulcus. Science Direct. [2021-06-02]. (原始內容存檔於2022-07-05) (英語).
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Gaillard, Frank. Superior temporal sulcus. Radiopaedia. [2021-06-02]. (原始內容存檔於2021-11-02) (美國英語).
- ^ Hein, Grit; Knight, Robert T. Superior temporal sulcus--It's my area: or is it?. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2008-12, 20 (12): 2125–2136 [2021-06-02]. ISSN 0898-929X. PMID 18457502. doi:10.1162/jocn.2008.20148. (原始內容存檔於2022-04-07).
- ^ 4.0 4.1 Isik, Leyla; Koldewyn, Kami; Beeler, David; Kanwisher, Nancy. Perceiving social interactions in the posterior superior temporal sulcus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2017-10-24, 114 (43): E9145–E9152 [2021-06-02]. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 29073111. doi:10.1073/pnas.1714471114. (原始內容存檔於2022-01-28) (英語).
- ^ 5.0 5.1 Leroy, François; Cai, Qing; Bogart, Stephanie L.; Dubois, Jessica; Coulon, Olivier; Monzalvo, Karla; Fischer, Clara; Glasel, Hervé; Van der Haegen, Lise. New human-specific brain landmark: The depth asymmetry of superior temporal sulcus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2015-01-27, 112 (4): 1208–1213 [2021-06-02]. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4313811
 . PMID 25583500. doi:10.1073/pnas.1412389112. (原始內容存檔於2022-04-02).
. PMID 25583500. doi:10.1073/pnas.1412389112. (原始內容存檔於2022-04-02).
- ^ Campbell, R.; MacSweeney, M.; Waters, D. Sign Language and the Brain: A Review. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education. 2007-06-14, 13 (1): 3–20. ISSN 1081-4159. doi:10.1093/deafed/enm035.
- ^ Zilbovicius, Monica; Meresse, Isabelle; Chabane, Nadia; Brunelle, Francis; Samson, Yves; Boddaert, Nathalie. Autism, the superior temporal sulcus and social perception. Trends in Neurosciences. 2006-07, 29 (7): 359–366 [2021-06-02]. ISSN 0166-2236. PMID 16806505. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2006.06.004. (原始內容存檔於2022-03-20).
- ^ Pure word deafness with auditory object agnosia after bilateral lesion of the superior temporal sulcus. Cortex. 2015-12-01, 73: 24–35 [2021-06-02]. ISSN 0010-9452. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2015.08.001. (原始內容存檔於2021-06-03) (英語).
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
